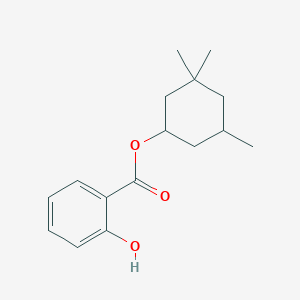
Homosalate is an organic compound used in some sunscreens. It is an ester formed from salicylic acid and 3,3,5-trimethylcyclohexanol, a derivative of cyclohexanol. C16H22O3 https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Homosalate#section=Top.
An oil-soluble chemical sunscreen agent that protects the skin from UVB (295-315 nm) with a peak protection at 306 nm. Homosalate is not a strong UV filter in and of itself (gives only SPF 4.3 protection at max. allowed 10% concentration) and it is not photostable (looses 10% of its SPF protection in 45 mins) so it always has to be combined with other sunscreens for proper protection. Its big advantage, though, is that it is a liquid and is excellent for dissolving other hard to solubilize powder sunscreen agents, like the famous Avobenzone.
Regarding Homosalate's safety profile, we do not have the best news. In-vitro (made in the labs) studies have shown that it might have some estrogenic activity. Do not panic, these studies were not conducted on real humans under real world conditions. Still, if you are a 'better safe than sorry' type, be careful when using Homosalate containing sunscreens long-term and full-body
https://incidecoder.com/ingredients/homosalate
Homosalate is an organic UV filter widely used in U.S. sunscreens. The FDA has proposed that there is insufficient data to evaluate whether it is safe and effective to use in sunscreens. Homosalate has been found to penetrate the skin, disrupt hormones and produce toxic breakdown byproducts over time (Krause 2012, Sarveiya 2004, SCCNFP 2006, Matta 2020).
A recent opinion from the European Commission found that homosalate was not safe to use at concentrations up to 10 percent and recommended a maximum concentration of 1.4 percent, because of concerns for potential endocrine disruption (SCCS 2020). The FDA allows U.S. sunscreen manufacturers to use it in concentrations up to 15 percent.
https://www.ewg.org/sunscreen/report/the-trouble-with-sunscreen-chemicals/
